TL;DR
The AI Futures team released an upgraded unified model for forecasting AI capability milestones, including Automated Coder (AC) and superintelligence (ASI). The new model lengthens the median estimate for full coding automation by roughly three years compared with their prior AI 2027 model, primarily because it is less optimistic about pre-full-automation R&D speedups.
What happened
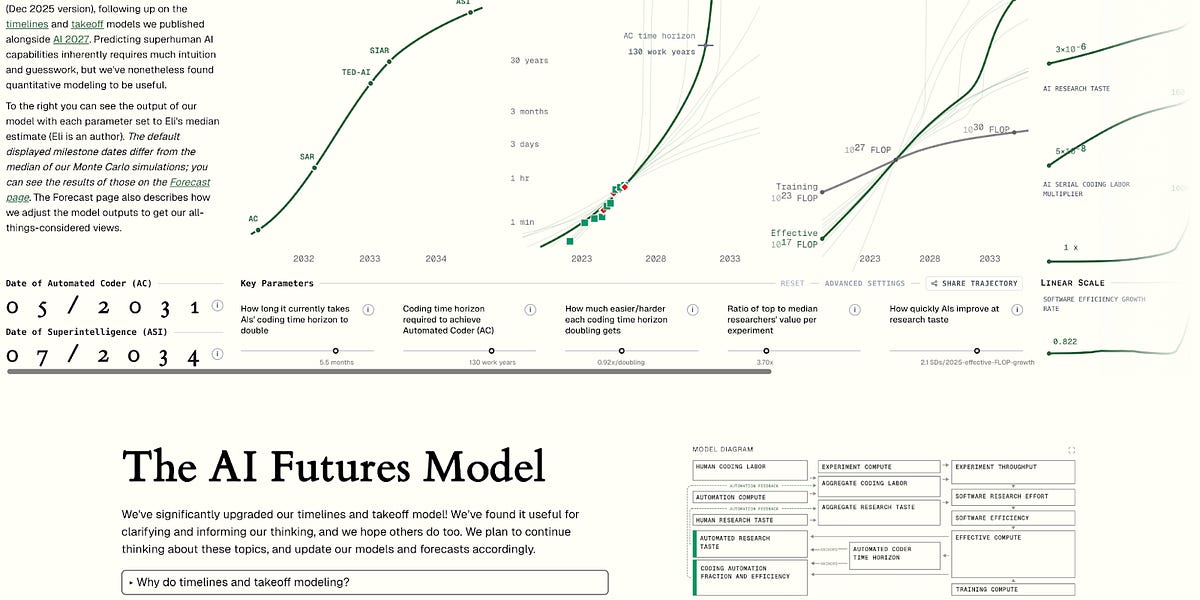
The AI Futures project published a December 2025 update that substantially revises its timelines and takeoff-speed models. The team consolidated multiple approaches into a unified forecasting framework that projects when systems will reach milestones such as Automated Coder (full coding automation) and ASI (far surpassing top human performance across cognitive tasks). Key changes include improved treatment of AI R&D automation and a new reliance on capability-benchmark trend extrapolation (notably METR-HRS) to set effective compute requirements. These model refinements produced a roughly 2–4 year shift in the median for full coding automation versus the April 2025 AI 2027 model, which the authors summarize as about a three-year longer timeline overall. The update keeps some parameters tied to data while leaving others as informed judgments and provides an interactive website so users can explore and modify assumptions.
Why it matters
- Revised timelines change expectations for when AI could fully automate software development and other high-skill tasks, affecting planning for industry and policy.
- A more explicit model of AI R&D automation alters how quickly improvements are expected to compound, which affects risk assessments and preparedness.
- Using benchmark trend extrapolation (METR-HRS) shifts the basis for effective-compute estimates away from brain-anchored analogies, changing the inputs to many forecast methods.
- The model’s transparency and adjustable parameters enable others to test alternative assumptions and incorporate new empirical evidence.
Key facts
- The update introduces a unified model that forecasts milestones like Automated Coder (AC) and artificial superintelligence (ASI).
- Compared with the AI 2027 model (Apr 2025), the new model’s median for full coding automation moved about 2–4 years later; the team summarizes this as roughly three years longer.
- The primary reason for the later timeline is reduced optimism about acceleration from AI R&D automation prior to full automation.
- The authors emphasize capability-benchmark trend extrapolation—using METR-HRS—to set the effective compute requirement for very capable AIs.
- Revenue extrapolation (Epoch dataset) was discussed: frontier AI revenue estimated around $20B and growing at ~4.1x/year, which simple extrapolation reaches ~$100T annualized revenue near the end of 2031.
- The update reviews alternative forecasting approaches: expert surveys (wide disagreement), bio-anchored compute estimates (e.g., Ajeya Cotra’s 2050 median), and other models (Davidson’s FTM and Epoch’s GATE with varied medians).
- Some model parameters are grounded in empirical data; others are intuitive or subjective and can be adjusted by users on the interactive site.
- The authors caution that no model is definitive and stress the importance of updating forecasts with new empirical data.
What to watch next
- New empirical results on METR-HRS and other capability benchmarks that would change effective-compute extrapolations.
- Evidence of AI R&D automation increasing the speed of software and hardware progress, which could shift timelines again.
- Future model updates and parameter revisions on the AI Futures interactive site as more data arrive.
Quick glossary
- Automated Coder (AC): A milestone denoting AI systems that can fully automate software development tasks at human or better levels.
- Artificial superintelligence (ASI): A hypothetical AI that significantly outperforms the best humans across virtually all cognitive tasks.
- METR-HRS: A suite of capability benchmarks and time-horizon measures used to extrapolate trends in AI performance, especially for coding tasks.
- Training compute: The amount of computational resources used to train a model; often used in forecasts relating compute to capabilities.
- AI R&D automation: The process by which AI tools and systems automate tasks in AI research and development, potentially accelerating overall progress.
Reader FAQ
Can I run the model myself?
Yes — the update points to an interactive website where users can adjust parameters and explore forecasts.
Why did the timeline shift later compared with the previous model?
The authors say the change mainly reflects a more conservative view of pre-full-automation AI R&D speedups—i.e., less optimistic assumptions about automation accelerating R&D.
Does the model give a single AGI date?
Not confirmed in the source.
Should we trust the model’s forecasts?
The authors caution the model is not definitive: some parameters are data-driven while others are subjective, and they encourage updating assumptions as new evidence appears.
AI Futures Model: Dec 2025 Update We've significantly improved our model(s) of AI timelines & takeoff speeds! DANIEL KOKOTAJLO, ELI LIFLAND, BRENDAN HALSTEAD, AND ALEX KASTNER DEC 31, 2025 86…
Sources
Related posts
- Straussian Memes: A lens on layered messaging and social self-stabilization
- Straussian Memes: How Multi-Level Messaging Enables Mass Persuasion
- Gemini 3.0 Deciphers 500-Year-Old Marginalia in Nuremberg Chronicle