TL;DR
Cursor developed Bugbot, an AI-driven code-review agent that inspects pull requests for logic, performance, and security issues. After 40 major experiments and architecture changes — including an agentic design and a custom 'resolution rate' metric — Bugbot's resolution rate rose from 52% to over 70% and the average bugs flagged per run climbed from 0.4 to 0.7.
What happened
Cursor built Bugbot to reduce manual code-review effort by analyzing pull requests for logic bugs, performance issues, and security vulnerabilities before code reaches production. Early efforts relied on qualitative iteration; as base models improved, the team explored multiple configurations of models, pipelines, filters, and context-management strategies. A multi-pass approach (eight parallel passes with randomized diff order) combined with majority voting and a validator model became an early effective flow. To operate at scale, the team rebuilt Git integration in Rust, added rate-limit monitoring, request batching, proxy infrastructure, and introduced Bugbot rules for codebase-specific invariants. Crucially, Cursor created a resolution rate metric — an AI-driven measure evaluated at PR merge time — which enabled systematic hill-climbing on real signal. Switching to a fully agentic architecture later in development drove further gains. Versions have progressed from v1 (July 2025) to v11 (January 2026), and the product now runs on millions of PRs per month for several customers.
Why it matters
- Provides a measurable signal (resolution rate) that shows whether flagged issues are actually fixed, moving beyond anecdotal feedback.
- Improves the yield of automated reviews: more real bugs are being identified and resolved per PR without a comparable jump in false positives.
- Scales to production workflows by addressing performance and integration constraints (Git integration, rate limits, batching).
- Allows teams to encode repo-specific rules, making automated reviews more relevant to complex codebases.
Key facts
- Cursor ran 40 major experiments that drove improvements in Bugbot's performance.
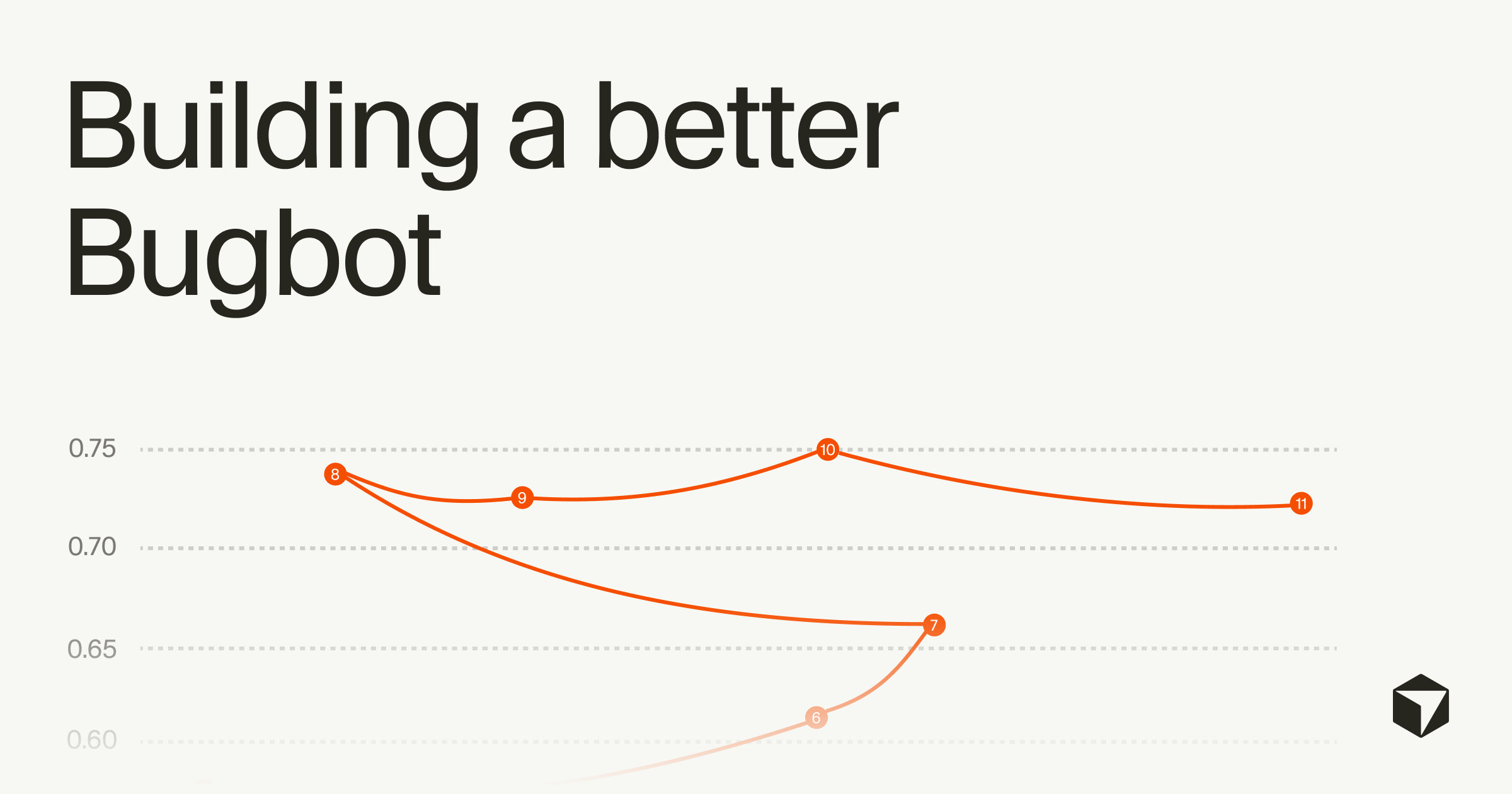
- Resolution rate increased from 52% to over 70% after iterative improvements.
- Average bugs flagged per run rose from 0.4 to 0.7, doubling resolved bugs per PR from ~0.2 to ~0.5.
- Initial effective flow included eight parallel passes with randomized diff order, majority voting, deduplication, and a validator model.
- Cursor rebuilt its Git integration in Rust and added rate-limit monitoring, request batching, and proxy-based infrastructure.
- Bugbot supports repository-specific 'rules' to encode invariants without hardcoding checks.
- The tool evolved to a fully agentic architecture that can call tools and fetch additional context dynamically.
- Cursor released Bugbot v1 in July 2025 and v11 in January 2026.
- Bugbot reviews more than two million PRs per month for customers that include Rippling, Discord, Samsara, Airtable, and Sierra AI.
- Cursor launched Bugbot Autofix in Beta to spawn Cloud Agents that attempt automatic fixes for issues found during reviews.
What to watch next
- Adoption and outcomes from Bugbot Autofix Beta — whether automated fixes reduce human review workload and maintain quality.
- Efforts to let Bugbot run code to verify its own bug reports and how that affects false positives and confidence.
- Experiments with an always-on scanning mode that continuously monitors codebases rather than waiting for pull requests.
- Arrival of new models and how combinations of models, harness design, and review structure influence future versions.
Quick glossary
- Resolution rate: An AI-driven metric that checks at PR merge time whether issues flagged by the tool were actually resolved in the final code.
- Agentic architecture: A design where an AI agent can reason, call tools, and decide runtime actions instead of following a fixed, linear pipeline.
- Pull request (PR): A request to merge code changes into a repository, commonly used as a review point in collaborative development.
- Validator model: A separate AI component used to re-check flagged issues and reduce false positives before reporting them.
Reader FAQ
What does Bugbot check for?
It analyzes pull requests for logic bugs, performance issues, and security vulnerabilities.
How effective is Bugbot?
Per the source, resolution rate rose from 52% to over 70%, and average bugs flagged per run increased from 0.4 to 0.7.
Which organizations use Bugbot?
The source lists customers including Rippling, Discord, Samsara, Airtable, and Sierra AI; Cursor also runs it on all internal code.
Can Bugbot automatically fix issues?
Cursor launched Bugbot Autofix in Beta, which spawns a Cloud Agent to attempt fixes for issues found during PR reviews.
Is Bugbot open source?
not confirmed in the source
Building a better Bugbot Jan 15, 2026 by Jon Kaplan in Research Table of Contents ↑ Humble beginnings From prototype to production Measuring what matters Hill-climbing Agentic architecture What's next…
Sources
- Building a better Bugbot
- Cursor 2.1: Plan Mode & Browser improvements, AI code reviews and more
- Bugbot | Cursor Docs
- Best practices for coding with agents
Related posts
- Wikimedia’s 25th birthday: lets more AI systems scan volunteer-built pages
- TSMC says AI chip demand will remain strong for at least two to three years
- Pocket TTS: 100M-parameter speech model that runs in real time on CPUs