TL;DR
A systems integration team built a one-way data transfer device using two Raspberry Pi units and an opto coupler to extract syslog and performance data from an air-gapped network. The design prioritises reliable delivery over throughput and uses UART for a stable, uni-directional link.
What happened
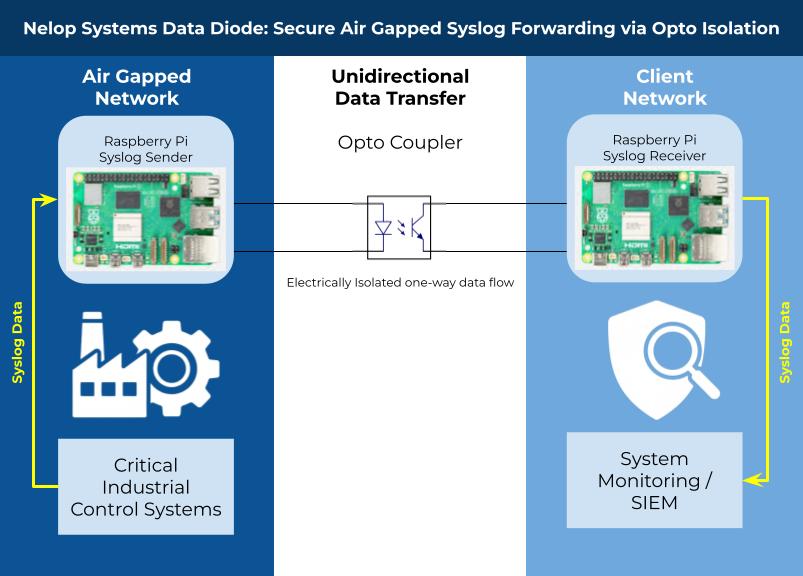
A client operating critical infrastructure and protected by an air gap needed a safe way to export operational logs and performance metrics for internal monitoring. The provider implemented a bespoke data-diode arrangement using two Raspberry Pi devices: one located inside the air-gapped environment to send data, and one on the external monitoring network to receive it. The Pis are connected through an opto coupler (opto isolator) that transmits signals via light, preventing a direct electrical connection and enforcing one-way flow. Custom scripts on both devices focus on reliable, ordered delivery of every log entry rather than maximizing throughput. The team initially tested a conventional serial approach but settled on a UART interface on the Raspberry Pi for simpler, more dependable single-direction communication. The resulting solution is presented as a tailored, low-cost method to give visibility into air-gapped systems without breaking the isolation.
Why it matters
- Maintains the physical isolation of air-gapped systems while allowing essential operational visibility.
- One-way hardware enforcement (opto coupler) reduces risk of data leakage or bidirectional compromise.
- Prioritising reliability over speed helps ensure critical logs are not lost, aiding security and uptime monitoring.
- A bespoke, low-cost buildable design can be adapted to legacy or constrained environments where commercial appliances may not fit.
Key facts
- Air-gapped networks are physically isolated and do not connect to the internet or external networks.
- The client required extraction of syslog and performance data from an air-gapped environment.
- The solution uses two Raspberry Pi units: a 'send' Pi inside the air gap and a 'receive' Pi outside it.
- An opto coupler (opto isolator) connects the Pis, allowing electrical signals to pass via light and enforcing one-way data flow.
- Custom scripts on both devices are tuned to ensure reliable transmission of log entries rather than high throughput.
- A standard serial port was tested but replaced by a UART interface on the Raspberry Pi for improved reliability.
- The implementation is described as a bespoke solution tailored to the client's specific operational and security needs.
- The post is published by Nelop Systems, which states over 25 years of experience and offers UK-based on-site service.
What to watch next
- Throughput is intentionally limited in favor of delivery reliability; expect lower data rates compared with bidirectional links.
- not confirmed in the source: formal security certification or third-party validation of the bespoke diode design.
- not confirmed in the source: long-term maintenance plans, firmware update processes, or managed support arrangements.
- not confirmed in the source: scalability limits or guidance for integrating multiple data diodes across larger deployments.
Quick glossary
- Air‑gapped network: A computer network physically isolated from other networks, including the public internet, to reduce exposure to remote attacks.
- Data diode: A hardware-based device that enforces one-way data flow between two networks, preventing information from traveling in the reverse direction.
- Opto coupler (opto isolator): An electronic component that transfers an electrical signal between two isolated circuits using light, avoiding direct electrical connections.
- UART: Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter; a serial communication interface used for simple point-to-point data exchange between devices.
- Syslog: A standard protocol for message logging used by operating systems and network devices to record system events and diagnostics.
Reader FAQ
Who built the data diode described in the post?
The implementation was delivered by the authoring organisation, Nelop Systems, based on the account in the source.
Does the solution preserve the air gap?
Yes. The design uses an opto coupler to enforce one-way transfer, maintaining the physical separation of the air-gapped network.
Why was UART chosen over a standard serial port?
After testing, the team found UART on the Raspberry Pi offered a simpler and more reliable one-way communication path than the standard serial setup.
Is the data diode commercially certified or independently audited?
not confirmed in the source
Creating a Bespoke Data Diode for Air Gapped Networks Published by on November 24, 2025 Air-gapped networks are physically isolated computer networks that do not connect to the internet or…
Sources
- Creating a Bespoke Data Diode for Air‑Gapped Networks
- Raspberry Pi Data Diode for One-Way UART Syslog Forwarding
- One-Way Data Extraction For Logging On Airgapped …
- Building an Affordable Data Diode to Protect Journalists
Related posts
- Vietnam bans unskippable video ads, requires skip after 5 seconds
- FTSE 100 bosses’ pay exceeds typical worker’s annual salary in under 3 days
- Palantir co-founder Joe Lonsdale endorses violent anti-communist tweet on X